The following are Brian Grim’s February 28, 2016, comments on the connection between religious freedom, sustainable development and mercy at fifth International Leaders Forum at the Vatican.
The following are Brian Grim’s February 28, 2016, comments on the connection between religious freedom, sustainable development and mercy at fifth International Leaders Forum at the Vatican.
Mercy, Sustainable Development and Religious Freedom: The Harmony of Caritas in Veritate, Dives in Misericordia, Laudato Si’, and Dignitatis Humanae
A rising tide of restrictions on religious freedom has engulfed the world, including in the United States, as shown by a series of ongoing studies by the Pew Research Center. In order to turn the tide, new and positive approaches are needed. The groundwork for these approaches, from one Catholic’s perspective, is to focus on the most powerful reason for religious freedom – that it sets people of faith free to do good.
In this perspective, mercy and love are essential to religious freedom. Indeed, in the Second Vatican Council’s declaration on religious freedom, Dignitatis Humanae, mercy and love provide critical – but underemphasized – theological foundations for religious freedom. The declaration promulgated by Pope Paul VI on December 7, 1965, asserts that there can be no compulsion in matters of religion and it roots the rightness of this freedom in human dignity, with the fundamental basis of this assertion being the mercy and love of Christ. Specifically, Dignitatis Humanae (section 11, paragraph 2b) states:
For [Christ] bore witness to the truth, but He refused to impose the truth by force on those who spoke against it. Not by force of blows does His rule assert its claims. It is established by witnessing to the truth and by hearing the truth, and it extends its dominion by the love whereby Christ, lifted up on the cross, draws all men to Himself.
In short, religious freedom is “right” because the love of Christ shown in the mercy extended to all through the cross is to be embraced freely and not through coercion.
Dignitatis Humanae itself does not, however, spend much time on mercy and love as shown by simple word counts. The title and text of the more than 5,000-word religious freedom declaration only mentions the term “love” five times while not mentioning the term “mercy” at all. By contrast, “free” or “freedom” is mentioned 68 times, “right” or “rights” is mentioned 48 times, “true” or “truth” is mentioned 40 times, “law” or “legal” is mentioned 11 times, as is the term “dignity.”
If mercy and love are central to religious freedom, then why are they given relatively little play in the declaration? Perhaps it was the 1965 historical context, a time at which global communist power and expansion was reaching an apex. In those days, the greatest threat to religious freedom was seen as the atheist attempt to eradicate the world of what Karl Marx called the opiate of the people, religion. Such Marxist critique was adopted by communist regimes from from the Soviet Union and East Germany to China and Vietnam, and from Castro in Cuba and FARC in Nicaragua to the People’s Republics in Angola and Mozambique. It even made some inroads within the Arab world.
Given this historical context, it is understandable that Dignitatis Humanae focused on juridical freedom with an emphasis on what G. del Pozo Abejón called the dual “negative rights” of immunity from coercion in conscience and immunity from being impeded from acting in conformity with conscience.
These protections are clearly important. But if the vision and practice of religious freedom is primarily focused on rights, it is much poorer than if it is centered on the positive virtues of mercy and love. Firmly rooting religious freedom in these virtues opens up the entire spectrum of possibilities to expand religious freedom in ways that contribute to the spiritual and integral human development of our world.
This is especially important in the post-communist world where religion-related hostilities arising from society itself are the greatest threats to religious freedom rather than the actions of communist states, though in China, North Korea and Cuba they still have powerful restrictions.
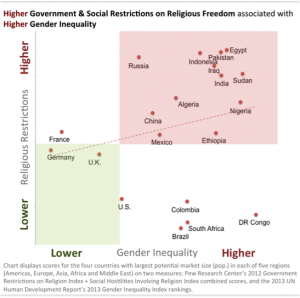
In a 2014 study I led when I was still at the Pew Research Center, we found for the first time that restrictions on religious freedom coming from social forces impacted a larger share of the world’s people than government restrictions on religious freedom. The study identified six specific types of social hostilities that made precipitous jumps. These included social harassment of women over religious dress, societal abuse of religious minorities, violent enforcement of religious norms by groups in society, mob violence related to religion, religion-related terrorist violence, and sectarian conflict.
Compounding the social challenge is that a growing segment of Western societies is religiously unaffiliated and no longer sees religion – and therefore religious freedom – as a basic force for good. The Pew Research Center study “‘Nones’ on the Rise,” for instance, reports that the number of Americans who are religiously unaffiliated now stands at one fifth of the adult population, while a third of adults under 30 are unaffiliated. Of the total unaffiliated, nearly 6% of the U.S. population identifies as atheist or agnostic, while 14% claim no particular religious affiliation. The Pew study found that a majority of the religiously unaffiliated say that they are ambivalent toward religious institutions and some express negative views of religious organizations. For instance, Pew found that a majority of the religiously unaffiliated think that religious organizations are too focused on such things as money and power, and on rules and politics.
The Pew study also found that only 45% of religiously unaffiliated people believe that congregations and religious institutions contributed some or a great deal to solving social problems, and 63% of atheists and agnostics said that religious institutions contributed not much or nothing at all to solving social problems.
This leads to two “ifs” and a “then”: if (a) social hostilities involving religion as mentioned above are now a greater challenge to religious freedom than government restrictions on religious freedom; and if (b) a majority of those outside of religious communities no longer see religion – and therefore religious freedom – as a basic force for good in society; then (c) we need a social approach to religious freedom that focuses on the main purpose of religious freedom – setting people of faith free to be incarnation of mercy and love, because, when people of faith are guided by and act on their conscience with “love, joy, peace, patience, kindness, generosity, faithfulness, gentleness, and self-control, against such there is no law” (Galatians 5:23).
This means that religious freedom must be much more than just protecting the dual “negative rights” of immunity from coercion in conscience and immunity from being impeded from acting in conformity with conscience. Religious freedom must be advanced by people of faith, motivated by their faith, working wholeheartedly for the common good.
In other words, the best way of advancing religious freedom today is not through legislation and litigation – though they play a part – but through the authentic love of neighbor (and even enemy) in response to the mercy and love of God to us all.
Pope Francis’s encyclical, Laudato si’, On Care for Our Common Home, states:
Jesus reminded us that we have God as our common Father and that this makes us brothers and sisters. Fraternal love can only be gratuitous; it can never be a means of repaying others for what they have done or will do for us. That is why it is possible to love our enemies. This same gratuitousness inspires us to love and accept the wind, the sun and the clouds, even though we cannot control them. In this sense, we can speak of a “universal fraternity.” We must regain the conviction that we need one another, that we have a shared responsibility for others and the world, and that being good and decent are worth it.
In Dives in Misericordia (Latin for “Rich in Mercy”), Pope John Paul II, put it this way:
The experience of the past and of our own time demonstrates that justice alone is not enough, that it can even lead to the negation and destruction of itself, if that deeper power, which is love, is not allowed to shape human life in its various dimensions. It has been precisely historical experience that, among other things, has led to the formulation of the saying: summum ius, summa iniuria. This statement does not detract from the value of justice and does not minimize the significance of the order that is based upon it; it only indicates, under another aspect, the need to draw from the powers of the spirit which condition the very order of justice, powers which are still more profound.
Fr. Richard Roach, a Jesuit who taught moral theology at Marquette University, translated summum ius, summa iniuria, as “the highest law can become the gravest injury, or, defense of the most important right can become the greatest injustice.”
I once moderated a public panel composed representatives of Christian think tanks that came together to discuss the way forward for religious freedom advocacy. As moderator, I took a bit of privilege, and mentioned how powerfully I had been impacted by the gospel reading for the previous Sunday – the parable of the Good Samaritan (Luke 10: 25-37). And pushing my privilege a bit more, I read it to the esteemed crowd, though I’m sure all had heard and read it many times before. But, at least for me, I saw the value of religious freedom in a whole new way upon encountering anew that parable. The Samaritan was a foreigner with a foreign religion, and because he was free to be and do good, a wounded man left for dead and bypassed by his own religious kin was lifted and healed and loved.
A true challenge of religious freedom today and any day is to see – with mercy and love – the God-given good in everyone, including foreigners with foreign religions.
As one way to unpack the mercy-and-love approach to religious freedom, I will share a poetic parable of my own. As a convert to Catholicism in 1994 after having been a Baptist missionary, one of the rich benefits and blessings that happened almost immediately was that I received the gift of tongues. But not in the charismatic sense. I began writing poetic stories as a way to understand the new world I’d entered. Here’s one that captures the value of freedom (best if read aloud). And, it will give balance to the other turn I took after becoming Catholic – becoming a quantitative sociologist who works with statistics and data.
The Parable of Baron von Dael and poor Gus
Baron von Dael was a very greedy man – a very greedy man indeed; but he hid his naughty vice from the foolish and the wise by tithing all his wealth religiously. But beyond this tepid token of his generosity, the Baron never helped another soul. Still, the Baron always said, “I pray the poor are fed!” and “Fortune for myself is not the goal! O no! Fortune for myself is not a goal!”
Now, the Preacher and the Doc and the Mayor and the Cop were indebted to the Baron for their pay, so the Baron called on them to be sure he’d always win if a threat should ever dare to come his way.
It is thus that poor Gus does now enter in this tale, for he made a food that very magic’ly has the power in itself to multiply itself so the buyer buys it once and then is free. Free! Yes, O free from the pain of hunger’s grip and free from sudden bell that death does ring. But for Baron von Dael who does make his wealth through sale of costly food that’s processed by machine, the invention of poor Gus caused a mighty rotten fuss in his profit-making fine food industry.
So the Baron did begin with fervor fast to spin a web of sticky lies, and here they be: The Cop said, “Gus is shady!” as the Doc said, “He is crazy!” while the Mayor said, “That Gus I cannot trust!” Then the Preacher filled the air with a holy, reverent prayer, “O dear Lord please keep such poison far from us!”
By the time that all these lies were thus sounded through the skies, the food that Gus was making caused a scare! So the food and recipe were both burned for all to see and poor Gus was sent forever far from there.
But in a far off land where the people lend a hand to anyone who travels in their way, Gus freely made his food, and that nation quickly grew to be the very most ingenious of that day.
Baron von Dael was a very greedy man – a very greedy man indeed; though he hid his naughty vice, Highland folk put him on ice when they read this selfsame story that you read. The moral of this tale is not one I can tell, but here is why the Baron’s in his tomb: Danger surely looms when a poet’s in the room because funny words on paper spell out doom sometimes; yes, funny words on paper spelled his doom.
So, the poet promises not to tell the moral of the tale, but taking off my poet’s hat, I’ll venture a few comments. First, I wrote this poetic parable over the course of two days, November 15-16, 1997, reflecting on a Genesis 1:12, “the earth brought forth every kind of plant that bears seed and every kind of fruit tree on earth that bears fruit with its seed in it. God saw how good it was.” I know that not everyone believes that God created the world and/or created in the way the Genesis story describes, but taking the story at face value, it struck me that God created a world filled with freely available ingredients for our sustenance, one “that very magic’ly has the power in itself to multiply itself so the buyer buys it once and then is free. Free! Yes, O free from the pain of hunger’s grip and free from sudden bell that death does ring.” What an act of mercy and love to create a world that could be nourished even without the “sale of costly food that’s processed by machine.”
Second, there’s a difference between business for success and business for good. Certainly the two can be identical at times, but at other times, it’s not so, especially when “the Preacher and the Doc and the Mayor and the Cop are indebted to the Baron for their pay.” Today, organizations as diverse as the United Nations, the World Economic Forum and the Holy See are calling for more responsible economic growth that is meaningful, inclusive and sustainable.
Some valuable insights from socially conscious business leaders are also helping to lead the way and are worth listening to. For example, Mark Wilson, CEO of Aviva, one of the UK’s oldest and largest insurance companies, describes his mission as to be a “good ancestor.” He looks back with appreciation for the service-oriented leadership of his 300-year company, and wants people to look back on him in 300 years as good ancestor.
The Genesis story of a good creation expands the time horizon much beyond 300 years, with an imperative that we responsibly steward the planet for all time to come. Pope Francis’s encyclical, Laudato si’, calls on Catholics to join hands with others in this task.
Given the complexity of the ecological crisis and its multiple causes, we need to realize that the solutions will not emerge from just one way of interpreting and transforming reality. Respect must also be shown for the various cultural riches of different peoples, their art and poetry, their interior life and spirituality. If we are truly concerned to develop an ecology capable of remedying the damage we have done, no branch of the sciences and no form of wisdom can be left out, and that includes religion and the language particular to it. The Catholic Church is open to dialogue with philosophical thought; this has enabled her to produce various syntheses between faith and reason. The development of the Church’s social teaching represents such a synthesis with regard to social issues; this teaching is called to be enriched by taking up new challenges (Laudato si’, 63).
By joining others in advancing arguments from faith (and faiths), we are at the same time expanding the realm in which religion has a free and welcome voice in the urgent matters of today.
My third comment on the poetic parable of Baron von Dael and Gus is that innovation often comes from those outside the system. Having worked for decades in predominantly Muslim and Communist nations, I’ve experienced the positive role of diversity, including religious diversity. At least, I think that my having been a Christian minority in majority-Muslim and -Communist countries added something positive to those societies. The same positive contribution also comes from minorities living and working in Christian-majority lands. Indeed, there are millions of Good Samaritans – foreigners with foreign religions – regularly lifting and healing and loving people beyond their faith communities, including many Gus’s “in far off lands” freely plying their trade in ways that build the common good.
Integral in a mercy-and-love approach to religious freedom is openness to the ideas of others. For instance, Catholic Christians are convinced that our traditions, beliefs and actions have something to offer to the common good of all. A mercy-and-love approach to religious freedom opens our eyes and hearts to how the traditions, beliefs and actions of others can do the same. That doesn’t mean that I do not believe that Jesus Christ, “whom God raised from the dead” is the cornerstone of faith and that “there is no salvation through anyone else, nor is there any other name under heaven given to the human race by which we are to be saved” (Acts 4: 10b;12-13). I believe that – it’s what makes me a Christian. But equally, that doesn’t mean that the traditions, beliefs and actions of others can’t open my eyes to new thoughts and practices that help me and others progress spiritually and temporally.
This openness to working with and learning from others is especially appropriate in the 21st century. Recent research done by the Religious Freedom & Business Foundation as part of a “toolkit” being developed by members of the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council on the Role of Faith to increase “religious literacy” in our complex world, shows that the 21st century is projected to not only be more religious but also much more religiously diverse.
The study finds that religious populations are projected to outgrow religiously unaffiliated populations worldwide by a factor of 23 between 2010 and 2050. This will increase religious diversity and alter the distribution of wealth, with Hindu populations projected to see the greatest economic gains and Muslim populations making the greatest numeric gains. The study concludes that this growing religious diversity can be positive for the common good, but only if religious, national and business leaders promote interfaith understanding, protect minority groups’ human rights, and advance freedom of religion and belief, thereby ensuring sustainable, peaceful and integral human development for all.
Pope Emeritus Benedict XVI in Caritas in Veritate extends the connections between love and religious freedom to also include development. “Development requires attention to the spiritual life, a serious consideration of the experiences of trust in God, spiritual fellowship in Christ, reliance upon God’s providence and mercy, love and forgiveness, self-denial, acceptance of others, justice and peace.”
Benedict specifically observes in Caritas in Veritate that there “is another aspect of modern life that is very closely connected to development: the denial of the right to religious freedom. … Violence puts the brakes on authentic development and impedes the evolution of peoples towards greater socio-economic and spiritual well-being.”
A recent study backs up Benedict’s assertion, showing that religious freedom is an unrecognized asset to economic recovery and growth. The study, “Is Religious Freedom Good for Business?: A Conceptual and Empirical Analysis,” examined and found a positive relationship between religious freedom and ten of the twelve pillars of global competitiveness, as measured by the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Index. Moreover, the study went beyond simple correlations by empirically testing and finding the tandem effects of government restrictions on religion and social hostilities involving religion (as measured by the Pew Research Center) to be detrimental to economic growth while controlling for 23 other theoretical, economic, political, social, and demographic factors.
The study also furthers previous work in the field, including The Price of Freedom Denied (Brian J. Grim & Roger Finke, Cambridge, 2011), which showed that religious freedom is a key ingredient to peace and stability, as measured by the absence of violent religious persecution and conflict. This is particularly important for development because where stability exists, there is more opportunity to invest and conduct normal and predictable business operations, especially in emerging and new markets.
The study, “Is Religious Freedom Good for Business?” observes that religious hostilities and restrictions create climates that can drive away local and foreign investment, undermine sustainable, integral human development, and disrupt huge sectors of economies. Such has occurred in the ongoing cycle of religious regulation and hostilities in Egypt, which has adversely affected the tourism industry, among other sectors. Perhaps most significant for future economic growth, the study notes that young entrepreneurs are pushed to take their talents elsewhere due to the instability associated with high and rising religious restrictions and hostilities.
Let me conclude with an example of one way the Religious Freedom & Business Foundation is employing the mercy-and-love approach to advance religious freedom. As I mentioned already, the pressing challenges to religious freedom today are rising religious hostilities and the belief that religion is not a force for good in society. Therefore, we need to enlarge the space for and acceptance of religious freedom by, among other efforts, helping people of faith work together across faith and belief boundaries to meet the real needs of their neighbors.
The Religious Freedom & Business Foundation is currently adapting for interfaith use a denomination-based community and family jobs, education, and business enterprise curriculum originally developed by The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints to help new members in Africa and Latin America. The tool can be used to help young families, single adults, and adults in transition (including refugees) to get a job that fulfills their vocation or calling, obtain the skills to start or grow a business, or identify the education they need to get that job or run the business. The curriculum has already been used more than a million times throughout the world in a denominational setting. Now, working with an interfaith team including Christians of multiple denominations, Muslims of multiple backgrounds, Humanists, Hindus, Buddhists, Sikhs, Jewish people, and Baha’is, we are adapting the materials so that scriptural and faith principles from each tradition are part of a new interfaith resource called Empowerment+.
The Empowerment+ toolkit is intentionally designed to be used in a group (eliminating isolation), to provide practical results (overcoming desperation), to demonstrate acceptance (ending rejection), and to model the radical spiritual power of serving others (replacing spiritual anomie with spiritual groundedness). Integration and empowerment can help those experiencing a wide range of socio-economic risks including displacement, unemployment, isolation, crime, addiction and radical extremist violence.
The very act of putting scriptures and faith principles from multiple religions side-by-side is an act of love and respect. And, it requires mercy rather than judgement in order for it to be accepted by people from very different backgrounds. In doing so, faith communities will counter the suspicion and isolation that breeds extremism by putting forth the very reason why faith matters so much to so many people – faith cares not only for the spiritual needs of people, but for their temporal wellbeing as well, resulting in sustainable, meaningful and integral human development. And where there is religious freedom, people of faith are much freer to do this good – and that’s why I believe that the most important reason to advance religious freedom is because it sets people of faith free to do good.
 SALT LAKE CITY — Everyone has a stake in protecting religious freedom because it contributes to better economic and business outcomes, Elder D. Todd Christofferson of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles of the LDS Church said Friday. (Reported by Tad Walch, Deseret News)
SALT LAKE CITY — Everyone has a stake in protecting religious freedom because it contributes to better economic and business outcomes, Elder D. Todd Christofferson of the Quorum of the Twelve Apostles of the LDS Church said Friday. (Reported by Tad Walch, Deseret News)